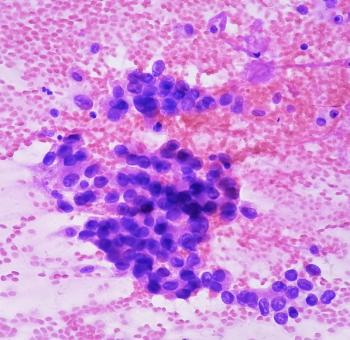
Interim trial data presented at the 2025 World Conference on Lung Cancer shows pumitamig’s promising efficacy in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).

Interim trial data presented at the 2025 World Conference on Lung Cancer shows pumitamig’s promising efficacy in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).

Cemiplimab was also superior in improving progression-free survival, objective response rate, and duration of response in patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Promising phase 2 results for taletrectinib in ROS1+ lung cancer show significant tumor shrinkage and manageable adverse effects.

A recent phase 3 study reveals osimertinib combined with chemotherapy offers unprecedented survival rates for patients with advanced EGFR-mutated lung cancer.
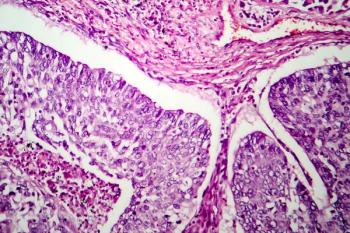
When combined with an anti–PD-L1 therapy, tarlatamab significantly improves overall survival in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
The treatment was generally well-tolerated in patients with ROS1-positive (ROS1+) non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

Shirish Gadgeel, MD, discusses the promising results of the randomized phase 3 HARMONi-2/AK112-303 study comparing ivonescimab to pembrolizumab in PD-L1–positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer.

Longer-term data from the phase 3 MARIPOSA trial confirm superior outcomes of a chemotherapy-free amivantamab-vmjw plus lazertinib regimen compared to osimertinib monotherapy as first-line therapy.

At the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer, Ana Baramidze, MD, PhD, presented 5-year outcomes of the trial, which investigated cemiplimab monotherapy in first-line advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with PD-L1 expression of 50% or greater.

At the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer, Benjamin Besse, MD, PhD, discussed the findings of the phase 3 CARMEN-LCO3 trial, which led to the discontinuation of the study drug by the manufacturer.

The combination of amivantamab and lazertinib showed improved intracranial efficacy, progression-free survival, and overall survival for non-small cell lung cancer.
Christian Rolfo discusses 6 different treatment options that are being developed across immunotherapies and antibody drug conjugates for non–small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer.
An overview of the potential treatment strategies for patients were presented at the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Promising abstracts surrounding DLL3 targeting for patients with lung and neuroendocrine cancer were presented at WCLC 2024.
As of May 2024, follow-up and exploratory analyses of MARIPOSA show improvements in outcomes for patients with EGRF-mutated non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

In a session at the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer, presenters highlight the most significant developments in local therapy for metastatic non–small cell lung cancer and advanced disease.
An overview of the latest developments in targeting DLL3 in lung neuroendocrine tumors were presented at the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Highlights from multiple trials investigating novel treatments for mNSCLC were presented at 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Presentations highlighted the potential of tarlatamab in treating solid tumor cancers.
Datopotamab deruxtecan was effective in patients with TROP2-QCS biomarker-positive tumors for non–small cell lung cancer
Lazertinib with amivantamab was found to be similar in efficacy to osimertinib in the MARIPOSA study.

Sotorasib (Lumakras) plus carboplatin and pemetrexed shows promise in the first line treatment of advanced non–small cell lung cancer.
The study met its primary endpoint of progression-free survival, and overall survival is continuing to be evaluated.