Allergy
Latest News
Latest Videos

Podcasts
CME Content
More News

The CLEAR framework helps guide pharmacists during the process of assessing and delabeling β-lactam allergies to improve patient outcomes.
Pharmaceutical companies must consider formulation, packaging, and labeling from the start to minimize errors and protect patients.

Azelastine, commonly used in nasal sprays to combat allergies, was found to reduce the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 among healthy controls in a phase 2 trial.

The "farm effect" is a term researchers use to describe the protective impact of growing up on traditional farms—especially around livestock, barns, and raw farm environments—on the development of allergies and asthma.

The biosimilar showed similar efficacy, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, quality of life, and immunogenicity in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU).

The FDA is warning of rare severe itching after stopping long-term use of popular allergy medications cetirizine and levocetirizine, urging patient education.

Sebetralstat becomes the first FDA-approved oral treatment for hereditary angioedema (HAE), offering rapid relief for patients experiencing acute attacks.
A pharmacist-led program effectively reduces incorrect penicillin allergy labels, promoting better antibiotic use and enhancing patient care in intensive care units.
About 10% of patients report a penicillin allergy, but only around 1% are truly allergic. Recommending penicillin allergy testing can help patients determine whether they have a true allergy.

New findings show LYR-210's potential to significantly alleviate chronic rhinosinusitis symptoms, offering hope for patients with nasal inflammation and polyps.

Pharmacists improve outcomes by clarifying and delabeling inaccurate antibiotic allergies.

Omalizumab expands its role in allergy management, now FDA-approved for food allergies, showcasing potential for broader applications in allergic rhinitis.

Jennifer Guthrie, RPh, district leader at CVS pharmacy describes the different medications to treat allergy symptoms and highlight how CVS stands out when addressing patients’ needs.
NS-229 is a Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor being investigated in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, a rare autoimmune condition that can cause severe allergic and asthmatic symptoms through inflammation of nerve cells.

The smartphone application-led delabeling also did not delay surgeries or procedures in the evaluated clinics.

Children who received antibiotics between birth and 2 years of age were more likely to develop food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma, but not neurodevelopmental conditions.
FDA Approves Dupilumab, Marking First Targeted Therapy in a Decade for Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Multiple phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated dupilumab’s (Dupixent; Regeneron, Sanofi) effectiveness in reducing hives and itch in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria compared with placebo.
Authors of a review published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology emphasized that blood eosinophil count and fractional exhaled nitric oxide cannot be relied on.

In mouse models, researchers identified that immune cells within the intestine may prevent unwarranted attacks against harmless food allergens.

At 12 and 24 months, there were 56.9% and 73.5% reductions in food-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE).


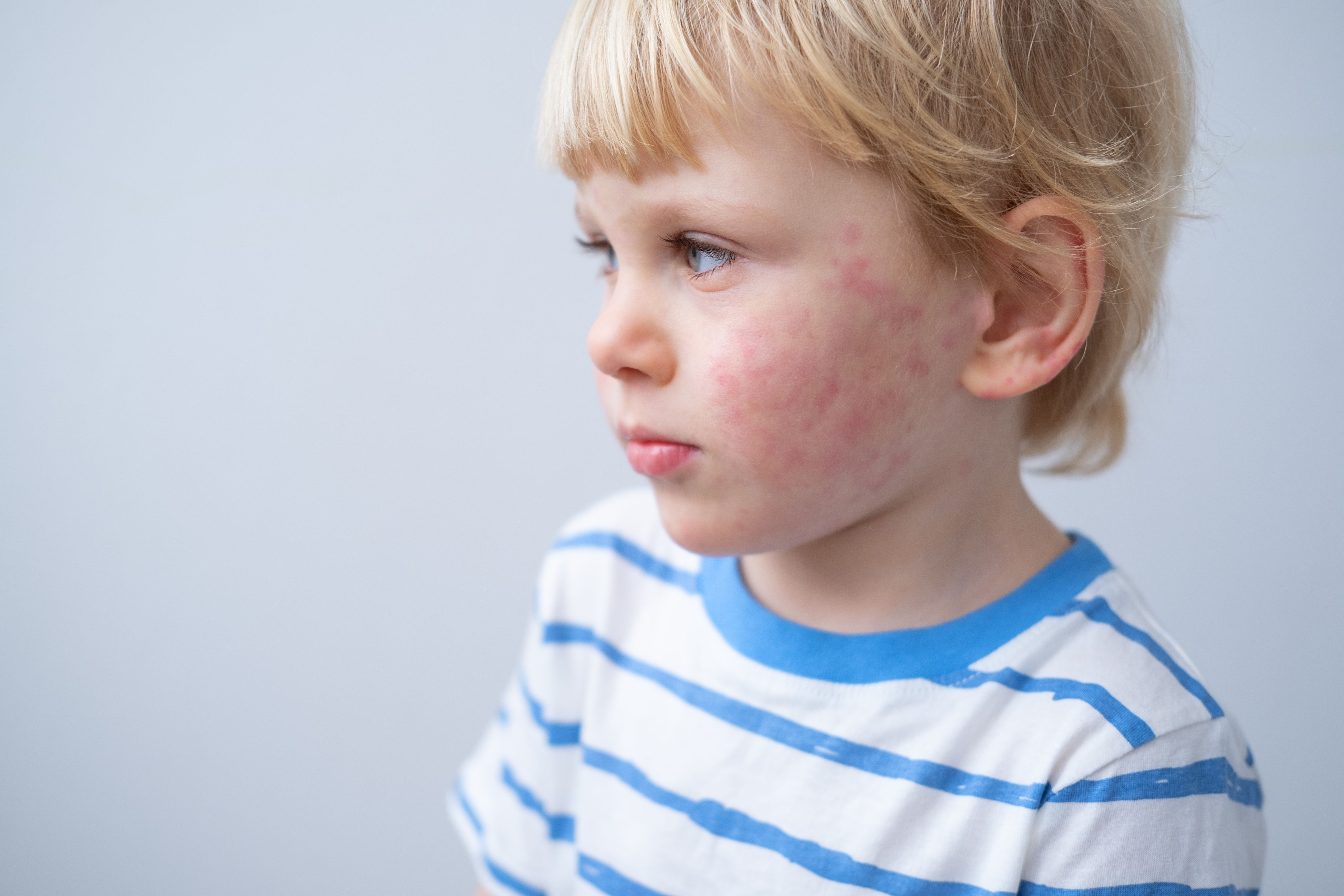
Symptoms occur when airborne irritants enter the eyes, nose, and throat, causing an allergic reaction.

Approximately 74% of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps receiving depemokimab across 2 trials did not need additional intervention.
Although dietary changes have historically been a key approach to managing eosinophilic esophagitis, their limitations highlight the need for pharmacologic treatments.

The authors note that further research is needed to clarify cost-effectiveness, long-term adherence, and psychosocial impacts of oral immunotherapy.